Bone
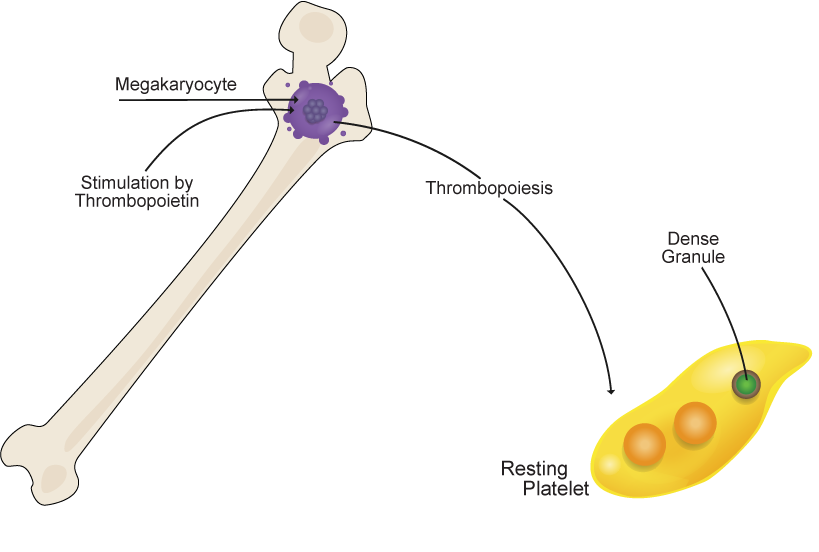
Platelets are produced by megakaryocytes in the bone marrow.
-
Dense granules are storage organelles for serotonin, ATP, ADP, phosphate and calcium.
Serotonin is not present in newly produced platelets.
-
Platelets are cytoplasmic fragments of megakaryocytes (MKs).
MKs are large polyploid stem cells in the bone marrow.
One MK can make 2-3,000 platelets.
-
New platelets have the discoid shape of resting platelets.
They are fragmented off MKs without nucleus and serotonin.
New platelets contain all granules such as α‐ and dense granules.
Platelets are unique to mammals. Animals that evolved before mammals have thrombocytes in their blood.
-
Thrombopoietin (TPO) is a chemical produced by the liver and kidney.
It stimulates MKs to produce platelets.
-
Thrombopoiesis is the process of platelet formation.
Healthy megakaryocytes produce discoid, functional platelets.
New platelets contain dense granules without serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). Serotonin is produced in the gut, released into the blood, and taken up by platelets.
Serotonin is needed for body temperature regulation – and thus is related to fever – and proper hemostasis as we know from rare disorders like Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome.